Prashant Pundir
Astonishing Robotics Facts You Didn’t Know About
“We’re fascinated with robots because they are reflections of ourselves”
– Ken Goldberg
Is it possible that robots are true representations of us? What did the first robot look like? What exactly does the term “robot” imply? Here you may learn about amazing robot trivia, history, and much more.
Everyone nowadays is familiar with robots. We don’t think of them as human-shaped bots seeking to take over all humanity because they’re so widespread. Robots are generally operated by a human or obey pre-programmed commands to make human activities easier.
“Researchers predict that by 2040, robots will be as intelligent as humans. Japan intends to have one million industrial robots by 2025. Human-robot marriage could be allowed in the United States by 2050, according to experts. Scientists in Australia are developing a microbot that can mimic the swim stroke of E. Coli bacteria. It will be used to take a biopsy from the interior of a patient using an injection.”
Robots today are a center of attraction, from our households to complex military conditions, and are likely to improve over time. Even if we are acquainted with robots, there are a few important observations about them that we’d have overlooked over the years of their growth and evolution.
Here are some interesting facts, observations, and trivia about robots –
The Term ‘Robot’
The term “robot” comes from the Czech word “robota,” which implies “forced labor.” The definition has evolved to include everything man-made capable of performing tasks as well as other human functions.
The Term “Robotics”
Robotics is a field of engineering and computer science that is multidisciplinary. Robotics is the study of the design, manufacture, administration, and application of robots. Robotics aims to create devices that can support and help humans.
It’s no longer simply about singular robots. As a field, robotics has resulted in the production of armies of robots that serve in a variety of capacities.
In 2012, Amazon paid $775 million for Kiva Systems, a robotics firm. Kiva’s robots help Amazon become more productive by automating the picking and packing procedure in big warehouses. The robots, which stand 16 inches tall and weigh approximately 145 kilograms, can run at 5 miles per hour and transport items weighing up to 317 kilograms.
Amazon now employs over 200,000 mobile robots in its warehouse infrastructure, in addition to the large numbers of human labor.
In addition to that, The Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (or SRMS)—also known as Canadarm—is one of the most key discoveries and valuable contributions from Canadian Aerospace engineers.
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA) launched a set of specially adapted robotic arms that were deployed on NASA space shuttle orbiters under the moniker Canadarm.
“The Canadarm was a remote-controlled mechanical arm, also known as the Shuttle Remote Manipulator System (SRMS). During its 30-year career with NASA’s Space Shuttle Program, the robotic arm deployed, captured and repaired satellites, positioned astronauts, maintained equipment, and moved cargo.”
Robotics as an industry has grown throughout the years and the utilization of service robots is fueled by rising wages, a lack of trained people, and an increasing acceptance of service applications in the military, medicine, and farming. In addition, the number of service robot producers who are providing advanced and innovative functionality has grown. Manufacturers can use robotic systems to support elderly workers and make working easier for people.
Robots & History
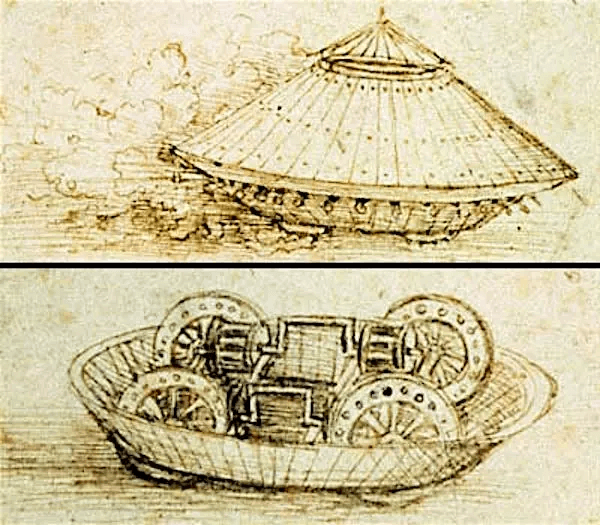
Da Vinci’s car
Da Vinci’s car is another fascinating truth about robotics. Leonardo Da Vinci constructed a car in 1478, but it was only supposed to be displayed as a work of genius. The vehicle was a self-driving spring system that might alternatively be referred to as the very first tank.
Da Vinci’s car
Renaissance-style robots
Given the number of brilliant innovations and wonderful sketches he produced during his lifetime, Leonardo Da Vince remains a mystery. Around 1495, he created a thorough idea for a mechanical warrior, which he drew out.
Despite the limitations imposed by today’s sources of power, he created designs for a robot with human structures.
Plans and Inventions by Leonardo Da Vince
The term “robot” used for the first time
Even though the term “robot” had been used earlier, it was originally used for man-made devices that worked independently in the 1920 drama R.U.R: Rossum’s Universal Robots. Karel Apek wrote the play, which depicts how robots conquer their owners.
The company that was the first to market robots
Unimation, established in 1956 by George Devol and Joseph Engelberger, was the first business to bring the very first set of industrial robots to the marketplace.
Robot – The first death
The renowned Azimov principles were prominently employed inside the film I, Robot, which centered around an examination into the first occurrence of a person being murdered by a robot.
In 1981, nevertheless, a Japanese industrial employee was squashed by a robot arm, which was the first documented unintentional death caused because of a robot.
Robots Stepping up the Game
People in the nineteenth century predicted that robots would be common in the twentieth century.
In the year 2000, the explosion of scientific breakthroughs and technological developments led several analysts to consider the future. As technology progressed, and visionaries began to view robots as common machines coexisting with people.
They envisioned robots undertaking and performing practically all of the tedious tasks of daily life, such as grooming, washing clothes, cleaning floors, vacuuming, and cooking food.
What’s the most intriguing part?
Numerous people across the world are already using robots to take care of mundane tasks.
Toy Robots
In the 1980s, the robotics business was growing, and most people could afford to buy robotic gadgets for their children. These play robots had a microcontroller that instructed them on how to dance, walk, and sing.
Toy robots nowadays are more complex than the intelligent robots of the 1980s.
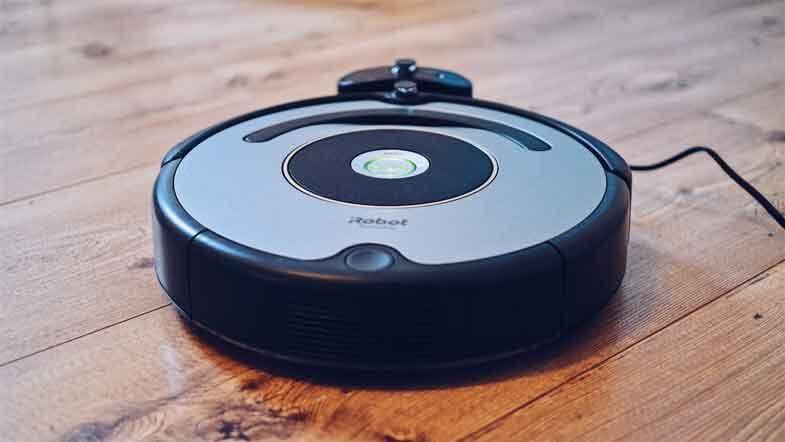
Vacuum Robots
During the end of the twentieth century, technology had progressed far enough to allow some basic robots to be used at home. Many researchers have started to launch robotic devices, but no one has been successful. A vacuum robot was the first and most effective robot for residential use. This robot was a vacuum cleaner that rotated in a circular motion.
Vacuum cleaning robots are now more popular than any other type of household robot. Millions of vacuum cleaning robots have been sold so far, and the number is continuously increasing.
A robot vacuum sweeper is known as a Roomba. There have been almost 15 million Roombas sold, sufficient for everybody in New York City and London.
Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots have long been a fascinating and much-anticipated type of robot. Engineers have already been tackling a slew of complex issues to create a functional humanoid robot.
Computer vision, balance systems, artificial intelligence, and battery timing were among the primary issues to be addressed. However, because of recent technological breakthroughs, researchers have been able to construct anything that could be classified as a real humanoid robot.
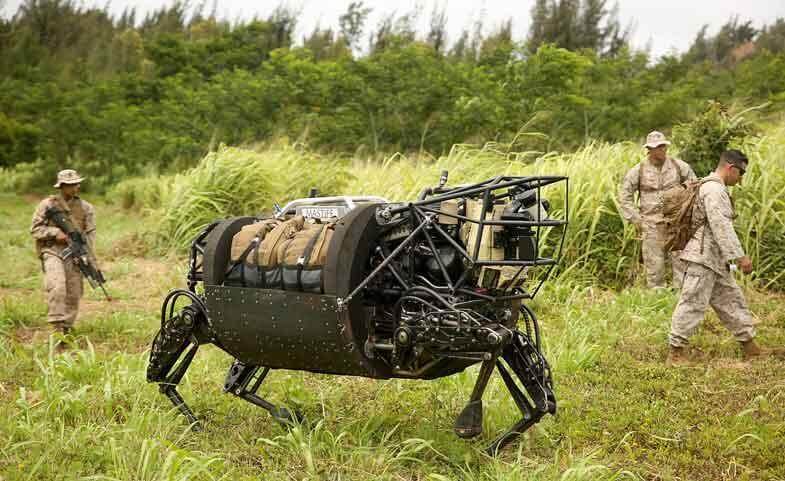
War Robots
Advances in the science of robotics are delivering not just convenience to human existence, but potentially extremely lethal autonomous war robots.
Drones and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) are among the most sophisticated unmanned aircraft and ground technologies in use today. The next step is to make them entirely or partially self-contained to assist the military in combat.
Military robot RIMPAC is under experimentation in 2014
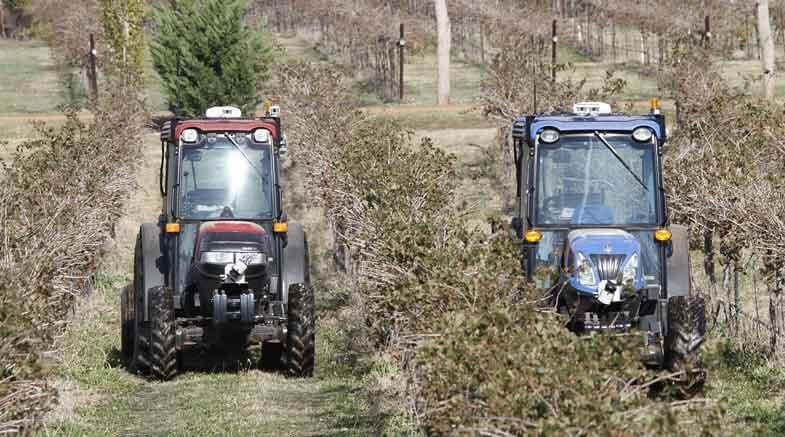
Agriculture Robots
Agriculture robots have already been successfully constructed and employed in the fields for seeding, caring for, and producing food. Growers are now deploying self-driving drones to detect crops that need to be protected against pests or harvested.
Autonomous agriculture robots are extremely power-saving and dramatically increase crop production. By 2020, it is expected that the majority of farmers in wealthy countries will be reaping and fertilizing their crops with robots.
Driverless autonomous spraying robots
Nanobots
Robots are extremely helpful devices that can perform tasks that humans cannot, and now Nanobots are available in really small sizes. These tiny robots, which typically range from 0.1 to 100 micrometers, are being used in fields such as medicine, research, and weapons.
Cyborg
Kevin Warwick, a cybernetics professor, invented the microchip that can be placed in the central nervous system. In 1998, he successfully implanted the chip inside his head.
The chip’s principal purpose is to send out signals controlled by the brain that may be recognized by a computer and used to accomplish tasks. As a result, he can control doors and other devices connected to him from afar.
Robot Body Parts
Several robotic prostheses have recently been installed on disabled people’s bodies. Many patients who have lost their hands, limbs, or legs in an accident have had robotic prostheses fitted successfully. The Robotic Prosthesis interprets brain signals and acts on them.
For example, if an individual wants to carry a pot of tea in his robotic hand, all he has to do is give it a thought, and a robotic arm will perform the task based on his brain impulses – just like a genuine arm.
Robots & Facts
- The terms “android” and “robot” are not equivalent. An android is a robot that has the appearance of a person.
- Robots, contrary to popular belief, do not have feelings or emotions. Sentient Robot, on the other hand, is a work in progress that looks at awareness and artificial intelligence.
- Elektro is the first humanoid robot in the world and featured in a movie released in 1960. The robot Elektro was created by the Westinghouse Electric Corporation.
- Shakey, the very first robot to employ artificial intelligence to make its judgments, was created in 1966.
- A cobot is a unique type of work robot that can operate alongside humans in workplaces while remaining safe. To train it, a person only needs to move their arms.
- The hitchBot is a robot that travels through cities and nations on its own. The first hitchBot made it across Canada and into Europe without incident.
- Human emotions can be influenced by robots. When a robot asked respondents not to switch it off in one experiment, roughly 30% of them obeyed the robot instead of the investigator.
- South Korea has the largest robot concentration of any country on the planet. There are around 631 robots for every ten-thousand employees in South Korea.
- Robear is a nursing robot that is described as a gentle bear capable of lifting an old person.
- Hanson Robotics created Sophia – the robot, which is an ever-evolving intelligent machine. At the Future Investment Initiative in Saudi Arabia in the fall of 2017, Sophia expressed its intention to coexist harmoniously with humans. Sophia the robot was granted Saudi Arabian citizenship on October 25, 2017.
- For more than three years, NASA’s robots ‘Spirit’ and ‘Opportunity’ have trudged across Mars, covering 10.5 miles.
In a Nutshell
Robotics is a diverse topic of discussion with such varied history, facts, and trivia. It is gaining rapid momentum in a plethora of industries and robots are all set to be an integral part of the future.
According to studies, there are already over 15% of 5 million tech-based job openings in the United States, and experts predict that as the trend continues, more and more jobs will require automation through applied robotics.
As a result, enrolling in a robotics course is a step toward future-readiness.